Techniques

We have a range of techniques to evaluate how the fish responds to invasion and damage. Some techniques, like qPCR, are very specific and targeted, providing us with detailed information on expression of certain genes. Other techniques, such as behavioural analyses, immunohistochemistry, histology and in vivo imaging give us insight into more general effects in the body.
Our overall aim is to obtain more knowledge on the immunological mechanisms and subsequent implications for the body. Using such approaches enable us to engineer novel and more cost-effective vaccines and obtain deeper understanding of immune responses. We have recently also implemented the CRISPR technique to be able to conduct functional studies on genes.
IHC is less used for zebrafish when compared to other fish such as rainbow trout and salmon. This is due to numerous available transgenic lines in zebrafish that can be used for functional studies. However, we work in both larvae and adult fish and especially in adults IHC can be very useful. We have antibodies against proliferative cells (PCNA), TCR, IgZ, Mpeg1, GFP, mCherry and a range of the pathogens we work with. It is possible to acquire more antibodies available for zebrafish on request.
Examples of investigations from our group using IHC in zebrafish can be found here:
Infection and immunity against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Real-time qPCR is a technique that measures the expression of genes (mRNA). We use this technique to measure gene expression e.g. after exposing fish to pathogens or a potentially harmful substance (e.g. nanoplastics, chemicals). Sampling is typically conducted over a time period and subsequent results reveal which type of immune response (Th1/Th2/Th17) is activated or whether a substance induces an inflammatory response. Examples of investigations from our group using qPCR on zebrafish can be found here:
Association between adaptive immunity and neutrophil dynamics in zebrafish (Danio rerio) infected by a parasitic ciliate.
Zebrafish Danio rerio as a model to study the immune response against infection with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis.
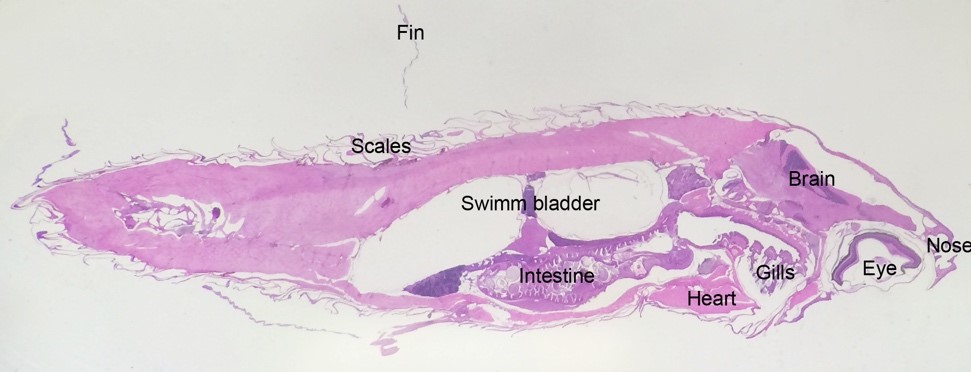
Histology is used to investigate pathological changes in the fish and for detecting invasive pathogens or foreign materials. We mostly use histology to investigate how cells and tissues react to damage and disease. Because the fish is so small we can section the whole adult zebrafish body and investigate all organs and tissues on a single slide.
Examples of investigations from our group using histology on zebrafish can be found here:
Infection and immunity against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
The FET (Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity ) test is a worldwide recognized test described by OECD https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-236-fish-embryo-acute-toxicity-fet-test_9789264203709-en. The test determines the median lethal dose (LC50 ), i.e. the concentration that kills 50% of the fish. Because only <5 days embryos are used for this test, no permit is needed from animal experimentation authorities. The whole test lasts 96 h and results in a curve depicting a dose-lethality correlation. Examples of investigations from our group using toxicological testing on zebrafish can be found here:

In vivo imaging is a unique and fantastic feature especially suited for zebrafish. Zebrafish is the only animal that allows an easy observation and video recording of biological processes in response to stimulus in live fish. This is one of the reasons why zebrafish have become very popular. We use a classical methodology when observing processes in transparent larvae by embedding them in a gel in which they are able to stay alive for approximately 24 h while being totally immobilized. We then investigate and document observations in the fish using a fluorescence confocal microscope. The adult fish are not transparent and visualization of cellular processes is only possible in the fins of live fish and for this purpose we have developed our own technique. Examples of investigations from our group using in vivo imaging on zebrafish can be found here:
Association between adaptive immunity and neutrophil dynamics in zebrafish (Danio rerio) infected by a parasitic ciliate.
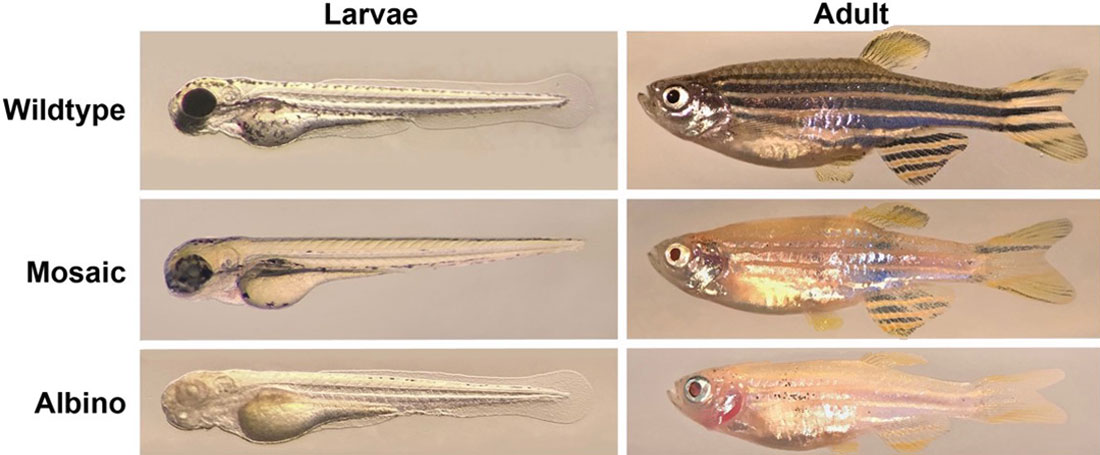

Zebrafish, in their larvae and adult stages, where the tyrosinase gene has been knocked out with CRISPR/Cas9. Photo by: Louise von Gersdorff Jørgensen and Moonika Haahr Marana.
We use the CRISPR/Cas technology for genome editing in zebrafish. We have created knock-out mutants for
genes encoding tyrosinase (tyr) and interferon regulatory factor 8 (irf8) to study certain biological function of the genes.
We inject embryos at the 1-cell stage to a create a mutation in the germ-line of zebrafish. The embryo injection generates the F0 line with mosaic mutation which we further outcross with the wild-type line to generate F1 heterozygous lines. Subsequently, we incross the F1 heterozygotes to obtain the F2 mutant line with homozygous mutation.
To check the efficacy of the genome editing we use heteroduplex mobility assay (HMA), T7 endonuclease 1 assay or sequence analysis of PCR amplicons.
